ICSE Mathematics Syllabus for Class 9: Students, you must be aware that the new academic session has begun and you should look for the syllabus of all the subjects covered in your curriculum. Being in 9th standard is quite important as from here the level will increase exponentially. You must learn how to get updated and keep your foot in the field. The very basic thing every student should know is the syllabus of their subjects. This helps them to keep real-time track of the syllabus covered and left. It also helps in self-studies as well. This article will discuss the latest syllabus for ICSE Class 9 Mathematics provided by the CISCE board. The paper code for the same is 51. As maths is one of the toughest and most important subjects, you need to maintain the pace from the beginning to cover and grasp its syllabus. Let us take you forward to the various aims of the Maths syllabus designed by the CISCE board for class 9 students.
ICSE Class 9 Mathematics Syllabus Aims:
1. To acquire knowledge and understanding of the terms, symbols, concepts, principles, processes, proofs, etc. of mathematics.
2. To develop an understanding of mathematical concepts and their application to further studies in mathematics and science.
3. To develop skills to apply mathematical knowledge to solve real-life problems.
4. To develop the necessary skills to work with modern technological devices such as calculators and computers in real-life situations.
5. To develop drawing skills, and skills of reading tables, charts and graphs.
6. To develop an interest in mathematics.
ICSE Class 9 Mathematics Highlights:
1. There will be one paper of two and a half hours duration carrying 80 marks and an Internal Assessment of 20 marks.
2. The paper will be divided into two sections, Section I (40 marks) and Section II (40 marks).
3. Section I: will consist of compulsory short answer questions.
4. Section II: Candidates will be required to answer four out of seven questions.
5. The solution of a question may require the knowledge of more than one branch of the syllabus
ICSE Class 9 Maths Syllabus 2023-24:
| Unit | Topics |
| 1. Pure Arithmetic | Rational and Irrational Numbers Rational, irrational numbers as real numbers, their place in the number system. Surds and rationalization of surds. Simplifying an expression by rationalizing the denominator. Representation of rational and irrational numbers on the number line. Proofs of the irrationality of √2√3 √5. |
| 2. Commercial Mathematics | Compound Interest (a) Compound interest as a repeated Simple Interest computation with a growing Principal. Use of this in computing Amount over a period of 2 or 3 years. (b) Use of formula . Finding CI from the relation CI = A – P.
|
| 3. Algebra | (i) Expansions Recall of concepts learned in earlier classes. (a ± b)2 (a ± b)3 (x ± a) (x ± b) (a ± b ± c)2 (ii) Factorisation a2 – b2 a3 ± b3 ax2 + bx + c, by splitting the middle term. (iii) Simultaneous Linear Equations in two variables. (With numerical coefficients only)
(iv) Indices/ Exponents Handling positive, fractional, negative and “zero” indices. Simplification of expressions involving various exponents amx am=am+n, am÷an=am-n, (am) n=amn etc. Use of laws of exponents. (v) Logarithms (a) Logarithmic form vis-à-vis exponential form: interchanging. (b) Laws of Logarithms and their uses. Expansion of expression with the help of laws of logarithms e.g. 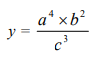 log y = 4 log a + 2 log b – 3 log c etc. |
| 4. Geometry | (i) Triangles (a) Congruency: four cases: SSS, SAS, AAS, and RHS. Illustration through cutouts. Simple applications. (b) Problems based on:
Proofs not required. (c) Mid-Point Theorem and its converse, equal intercept theorem (i) Proof and simple applications of mid- point theorem and its converse. (ii) Equal intercept theorem: proof and simple application. (d) Pythagoras Theorem Area-based proof and simple applications of Pythagoras Theorem and its converse. (ii) Rectilinear Figures (a) Proof and use of theorems on parallelogram.
(b) Constructions of Polygons Construction of quadrilaterals (including parallelograms and rhombus) and regular hexagon using ruler and compasses only. (c) Proof and use of Area theorems on parallelograms:
(iii) Circle: (a) Chord properties
(b) Arc and chord properties:
Note: Proofs of the theorems given above are to be taught unless specified otherwise. |
| 5. Statistics | Introduction, collection of data, presentation of data, Graphical representation of data, Mean, Median of ungrouped data. (i) Understanding and recognition of raw, arrayed and grouped data. (ii) Tabulation of raw data using tally-marks. (iii)Understanding and recognition of discrete and continuous variables. (iv) Mean, median of ungrouped data. (v) Class intervals, class boundaries and limits, frequency, frequency table, class size for grouped data. (vi) Grouped frequency distributions: the need to and how to convert discontinuous intervals to continuous intervals. (vii)Drawing a frequency polygon |
| 6. Mensuration | Area and perimeter of a triangle and a quadrilateral. Area and circumference of circle. Surface area and volume of Cube and Cuboids. (a) Area and perimeter of triangle (including Heron’s formula), all types of Quadrilaterals. (b) Circle: Area and Circumference. Direct application problems including Inner and Outer area. Areas of sectors of circles other than quarter-circle and semicircle are not included. (c) Surface area and volume of 3-D solids: cube and cuboid including problems of type involving:
|
| 7. Trigonometry | (a) Trigonometric Ratios: sine, cosine, tangent of an angle and their reciprocals. (b) Trigonometric ratios of standard angles - 0, 30, 45, 60, 90 degrees. Evaluation of an expression involving these ratios. (c) Simple 2-D problems involving one right-angled triangle. (d) Concept of trigonometric ratios of complementary angles and their direct application: sin A = cos (90 - A), cos A = sin (90 – A) tan A = cot (90 – A), cot A = tan (90- A) sec A = cosec (90 – A), cosec A=sec (90 – A) |
| 8. Coordinate Geometry | Cartesian System, plotting of points in the plane for given coordinates, solving simultaneous linear equations in 2 variables graphically and finding the distance between two points using distance formula. (a) Dependent and independent variables. (b) Ordered pairs, coordinates of points and plotting them in the Cartesian plane. (c) Solution of Simultaneous Linear Equations graphically. (d)Distance formula. |
Internal Assessment
A minimum of two assignments are to be done during the year as prescribed by the teacher.
Suggested Assignments
- Conduct a survey of a group of students and represent it graphically - height, weight, number of family members, pocket money, etc.
- Planning delivery routes for a postman/milkman.
- Running a tuck shop/canteen.
- Study ways of raising a loan to buy a car or house, e.g. bank loan or purchase a refrigerator or a television set through hire purchase.
- Cutting a circle into equal sections of a small central angle to find the area of a circle by using the formula A = πr2.
- To use flat cutouts to form cube, cuboids and pyramids to obtain formulae for volume and total surface area.
- Draw a circle of radius r on a ½ cm graph paper, and then on a 2 mm graph paper. Estimate the area enclosed in each case by actually counting the squares. Now try out with circles of different radii. Establish the pattern, if any, between the two observed values and the theoretical value (area = πr2). Any modifications?
Hope that information was helpful for you. To get the complete syllabus in pdf format click on the link below.
| Download ICSE Class 9 Mathematics Syllabus 2024 PDF |
To get ICSE Class 9 related information check the links below:
.webp)