Periodic Table Chemistry: The periodic table of elements is a tabular arrangement of all known chemical elements, organised based on their atomic number, electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. Elements are placed in order of increasing atomic number, which is the number of protons in an atom's nucleus. The table is divided into rows called periods and columns called groups or families.
Key Features of the Periodic Table
- Periods: There are seven horizontal rows in the periodic table. Elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells.
- Groups: There are 18 vertical columns. Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties and the same number of electrons in their outermost shell.
- Element Symbols: Each element is represented by a unique one- or two-letter symbol, usually derived from its English or Latin name (e.g., H for Hydrogen, Au for Gold from "Aurum").
- Atomic Number: The atomic number, which indicates the number of protons in an atom, is displayed above the element symbol.
- Atomic Mass: The atomic mass, usually found below the element symbol, indicates the weighted average mass of an element's isotopes.
History of Periodic Table of Elements
- Johann Dobereiner, a German chemist, was the first to consider trends among element properties in the early 1800s.
- In 1829, Dobereiner identified similarities in the physical and chemical properties of several groups of three elements, called Triads.
- Dobereiner noted that the atomic weight of the middle element in each Triad was approximately halfway between the atomic weights of the other two, and its properties were also intermediate.
- Dobereiner's Law of Triads was dismissed as coincidental since it only applied to a few elements.
- In 1862, French geologist A.E.B. de Chancourtois arranged elements by increasing atomic weights and created a cylindrical table to show periodic property recurrence, but it gained little attention.
- John Alexander Newlands, an English chemist, proposed the Law of Octaves in 1865, observing that every eighth element had similar properties when arranged by increasing atomic weight.
- Newlands compared this to musical octaves but his Law of Octaves applied only up to calcium and was not widely accepted initially.
- Newlands was later awarded the Davy Medal in 1887 by the Royal Society, London.
- Dmitri Mendeleev (1834-1907) and Lothar Meyer (1830-1895) independently developed the Periodic Law in 1869, observing periodic similarities in element properties when arranged by atomic weight.
- Lothar Meyer plotted physical properties against atomic weight and found a repeating pattern, noting changes in the length of the pattern.
- By 1868, Lothar Meyer had a table resembling the Modern Periodic Table but published it after Mendeleev.
- Mendeleev is credited with publishing the Periodic Law, which states that the properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic weights.
- Mendeleev's work led to the development of the Modern Periodic Table, recognising periodic trends and allowing predictions of undiscovered elements.
Mendeleev’s work
- Mendeleev arranged elements in a table with horizontal rows and vertical columns based on increasing atomic weights.
- Elements with similar properties were placed in the same vertical column or group.
- Mendeleev’s classification system was more elaborate than Lothar Meyer’s, considering a broader range of physical and chemical properties.
- He emphasised the importance of periodicity, using similarities in empirical formulas and properties of compounds to classify elements.
- Mendeleev recognised that some elements did not fit his classification scheme if strictly ordered by atomic weight.
- He chose to ignore the atomic weight order when necessary, believing that atomic measurements might be incorrect, to keep elements with similar properties together.
Elements of Periodic Table
Here is a list of periodic table elements with their names, symbols, atomic numbers, atomic masses, number of electrons and protons in a tabular format:
| Atomic Number | Element Name | Symbol | Atomic Mass (u) | Electrons | Protons |
| 1 | Hydrogen | H | 1.008 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | Helium | He | 4.0026 | 2 | 2 |
| 3 | Lithium | Li | 6.94 | 3 | 3 |
| 4 | Beryllium | Be | 9.0122 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | Boron | B | 10.81 | 5 | 5 |
| 6 | Carbon | C | 12.011 | 6 | 6 |
| 7 | Nitrogen | N | 14.007 | 7 | 7 |
| 8 | Oxygen | O | 15.999 | 8 | 8 |
| 9 | Fluorine | F | 18.998 | 9 | 9 |
| 10 | Neon | Ne | 20.18 | 10 | 10 |
| 11 | Sodium | Na | 22.99 | 11 | 11 |
| 12 | Magnesium | Mg | 24.305 | 12 | 12 |
| 13 | Aluminum | Al | 26.982 | 13 | 13 |
| 14 | Silicon | Si | 28.085 | 14 | 14 |
| 15 | Phosphorus | P | 30.974 | 15 | 15 |
| 16 | Sulfur | S | 32.06 | 16 | 16 |
| 17 | Chlorine | Cl | 35.45 | 17 | 17 |
| 18 | Argon | Ar | 39.948 | 18 | 18 |
| 19 | Potassium | K | 39.098 | 19 | 19 |
| 20 | Calcium | Ca | 40.078 | 20 | 20 |
| 21 | Scandium | Sc | 44.956 | 21 | 21 |
| 22 | Titanium | Ti | 47.867 | 22 | 22 |
| 23 | Vanadium | V | 50.942 | 23 | 23 |
| 24 | Chromium | Cr | 51.996 | 24 | 24 |
| 25 | Manganese | Mn | 54.938 | 25 | 25 |
| 26 | Iron | Fe | 55.845 | 26 | 26 |
| 27 | Cobalt | Co | 58.933 | 27 | 27 |
| 28 | Nickel | Ni | 58.693 | 28 | 28 |
| 29 | Copper | Cu | 63.546 | 29 | 29 |
| 30 | Zinc | Zn | 65.38 | 30 | 30 |
| 31 | Gallium | Ga | 69.723 | 31 | 31 |
| 32 | Germanium | Ge | 72.63 | 32 | 32 |
| 33 | Arsenic | As | 74.922 | 33 | 33 |
| 34 | Selenium | Se | 78.971 | 34 | 34 |
| 35 | Bromine | Br | 79.904 | 35 | 35 |
| 36 | Krypton | Kr | 83.798 | 36 | 36 |
| 37 | Rubidium | Rb | 85.468 | 37 | 37 |
| 38 | Strontium | Sr | 87.62 | 38 | 38 |
| 39 | Yttrium | Y | 88.906 | 39 | 39 |
| 40 | Zirconium | Zr | 91.224 | 40 | 40 |
| 41 | Niobium | Nb | 92.906 | 41 | 41 |
| 42 | Molybdenum | Mo | 95.95 | 42 | 42 |
| 43 | Technetium | Tc | 98 | 43 | 43 |
| 44 | Ruthenium | Ru | 101.07 | 44 | 44 |
| 45 | Rhodium | Rh | 102.91 | 45 | 45 |
| 46 | Palladium | Pd | 106.42 | 46 | 46 |
| 47 | Silver | Ag | 107.87 | 47 | 47 |
| 48 | Cadmium | Cd | 112.41 | 48 | 48 |
| 49 | Indium | In | 114.82 | 49 | 49 |
| 50 | Tin | Sn | 118.71 | 50 | 50 |
| 51 | Antimony | Sb | 121.76 | 51 | 51 |
| 52 | Tellurium | Te | 127.6 | 52 | 52 |
| 53 | Iodine | I | 126.9 | 53 | 53 |
| 54 | Xenon | Xe | 131.29 | 54 | 54 |
| 55 | Cesium | Cs | 132.91 | 55 | 55 |
| 56 | Barium | Ba | 137.33 | 56 | 56 |
| 57 | Lanthanum | La | 138.91 | 57 | 57 |
| 58 | Cerium | Ce | 140.12 | 58 | 58 |
| 59 | Praseodymium | Pr | 140.91 | 59 | 59 |
| 60 | Neodymium | Nd | 144.24 | 60 | 60 |
| 61 | Promethium | Pm | 145 | 61 | 61 |
| 62 | Samarium | Sm | 150.36 | 62 | 62 |
| 63 | Europium | Eu | 151.96 | 63 | 63 |
| 64 | Gadolinium | Gd | 157.25 | 64 | 64 |
| 65 | Terbium | Tb | 158.93 | 65 | 65 |
| 66 | Dysprosium | Dy | 162.5 | 66 | 66 |
| 67 | Holmium | Ho | 164.93 | 67 | 67 |
| 68 | Erbium | Er | 167.26 | 68 | 68 |
| 69 | Thulium | Tm | 168.93 | 69 | 69 |
| 70 | Ytterbium | Yb | 173.05 | 70 | 70 |
| 71 | Lutetium | Lu | 174.97 | 71 | 71 |
| 72 | Hafnium | Hf | 178.49 | 72 | 72 |
| 73 | Tantalum | Ta | 180.95 | 73 | 73 |
| 74 | Tungsten | W | 183.84 | 74 | 74 |
| 75 | Rhenium | Re | 186.21 | 75 | 75 |
| 76 | Osmium | Os | 190.23 | 76 | 76 |
| 77 | Iridium | Ir | 192.22 | 77 | 77 |
| 78 | Platinum | Pt | 195.08 | 78 | 78 |
| 79 | Gold | Au | 196.97 | 79 | 79 |
| 80 | Mercury | Hg | 200.59 | 80 | 80 |
| 81 | Thallium | Tl | 204.38 | 81 | 81 |
| 82 | Lead | Pb | 207.2 | 82 | 82 |
| 83 | Bismuth | Bi | 208.98 | 83 | 83 |
| 84 | Polonium | Po | 209 | 84 | 84 |
| 85 | Astatine | At | 210 | 85 | 85 |
| 86 | Radon | Rn | 222 | 86 | 86 |
| 87 | Francium | Fr | 223 | 87 | 87 |
| 88 | Radium | Ra | 226 | 88 | 88 |
| 89 | Actinium | Ac | 227 | 89 | 89 |
| 90 | Thorium | Th | 232.04 | 90 | 90 |
| 91 | Protactinium | Pa | 231.04 | 91 | 91 |
| 92 | Uranium | U | 238.03 | 92 | 92 |
| 93 | Neptunium | Np | 237 | 93 | 93 |
| 94 | Plutonium | Pu | 244 | 94 | 94 |
| 95 | Americium | Am | 243 | 95 | 95 |
| 96 | Curium | Cm | 247 | 96 | 96 |
| 97 | Berkelium | Bk | 247 | 97 | 97 |
| 98 | Californium | Cf | 251 | 98 | 98 |
| 99 | Einsteinium | Es | 252 | 99 | 99 |
| 100 | Fermium | Fm | 257 | 100 | 100 |
| 101 | Mendelevium | Md | 258 | 101 | 101 |
| 102 | Nobelium | No | 259 | 102 | 102 |
| 103 | Lawrencium | Lr | 262 | 103 | 103 |
| 104 | Rutherfordium | Rf | 267 | 104 | 104 |
| 105 | Dubnium | Db | 270 | 105 | 105 |
| 106 | Seaborgium | Sg | 271 | 106 | 106 |
| 107 | Bohrium | Bh | 270 | 107 | 107 |
| 108 | Hassium | Hs | 277 | 108 | 108 |
| 109 | Meitnerium | Mt | 278 | 109 | 109 |
| 110 | Darmstadtium | Ds | 281 | 110 | 110 |
| 111 | Roentgenium | Rg | 282 | 111 | 111 |
| 112 | Copernicium | Cn | 285 | 112 | 112 |
| 113 | Nihonium | Nh | 286 | 113 | 113 |
| 114 | Flerovium | Fl | 289 | 114 | 114 |
| 115 | Moscovium | Mc | 290 | 115 | 115 |
| 116 | Livermorium | Lv | 293 | 116 | 116 |
| 117 | Tennessine | Ts | 294 | 117 | 117 |
| 118 | Oganesson | Og | 294 | 118 | 118 |
This table includes all 118 known elements, providing their names, symbols, and atomic numbers.
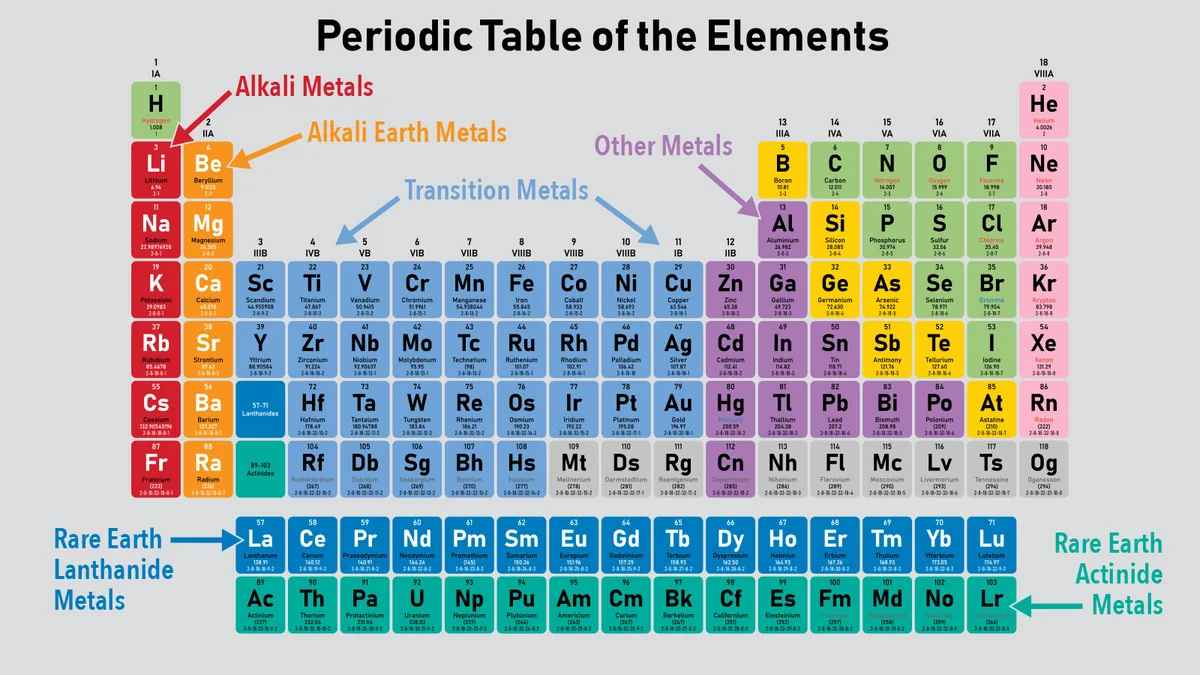
Image Source: yourdictionary.com
Classification of Elements of Periodic Table
Elements are grouped into four main categories: metals, nonmetals, metalloids, and noble gases. Here's a detailed classification:
- Metals
- Alkali Metals (Group 1): Highly reactive, especially with water (e.g., Lithium, Sodium, Potassium).
- Alkaline Earth Metals (Group 2): Less reactive than alkali metals, but still quite reactive (e.g., Beryllium, Magnesium, Calcium).
- Transition Metals (Groups 3-12): Includes elements like Iron, Copper, and Gold, known for their conductivity and malleability.
- Lanthanides: Rare earth elements, used in electronics and lasers (e.g., Lanthanum, Cerium).
- Actinides: Radioactive elements, some synthetic (e.g., Uranium, Plutonium).
- Nonmetals
- Hydrogen: Unique, not fitting into any single group.
- Halogens (Group 17): Very reactive nonmetals, form salts with metals (e.g., Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine).
- Other Nonmetals: Essential for life, such as Carbon, Nitrogen, and Oxygen.
- Metalloids
- Elements with properties intermediate between metals and nonmetals (e.g., Boron, Silicon, Germanium). These are often semiconductors.
- Noble Gases (Group 18)
- Inert gases, nonreactive due to having a complete valence electron shell (e.g., Helium, Neon, Argon).
Periodic Trends:
- Atomic Radius: Decreases across a period and increases down a group.
- Ionization Energy: Increases across a period and decreases down a group.
- Electronegativity: Increases across a period and decreases down a group.
Modern Periodic Law:
- States that the properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic numbers. This law is the basis for the modern periodic table.
Tricks to Learn Periodic Table Through Easy Mnemonic Phases
Check here the easy ways to remember the periodic table for Indian students. Source: Quora
Group 1: (Li Na K Rb Cs Fr)
- LiNa ne Kri RuBy Cse Friendship
Group 2: (Be Mg Ca Sr Ba Ra)
- Beta Maange Car Scooter Baap Razi
Group 3: (B Al Ga In Th)
- Baingal Aaalo Gajar In Thaila
Group 14: (C Si Ge Sn Pb)
- Chemistry Sir Gives Sanki Problems
Group 15: (N P As Sb Bi)
- Nana Patekar Aishwary Sab Bindass
Group 16: (O S Se Te Po)
- us se tepo
Group 17: (F Cl Br I As)
- Fir kal Bahar Aai Esi
Group 18: (He Ne Ar Kr Xe Rn)
- Hena ar kreen ki xeroz Rangeen
3d Series- (Sc Ti V Cr Mg Fe Co Ni Cu Zn)
- Science Teacher Very Cruel Mange Fees Copy Nikalo Copper Zinc
Creating mnemonic phrases can help you remember the order of elements, especially for the first 20 elements or specific groups.
First 10 Elements:
- Hydrogen (H), Helium (He), Lithium (Li), Beryllium (Be), Boron (B), Carbon (C), Nitrogen (N), Oxygen (O), Fluorine (F), Neon (Ne).
- Mnemonic: "Happy Henry Likes Beans Brown, Crusty, Not Over-Fried Nicely."
Group 1 (Alkali Metals):
- Lithium (Li), Sodium (Na), Potassium (K), Rubidium (Rb), Cesium (Cs), Francium (Fr).
- Mnemonic: "Little Naughty Kids Rub Cats Fur."
Group 17 (Halogens):
- Fluorine (F), Chlorine (Cl), Bromine (Br), Iodine (I), Astatine (At).
- Mnemonic: "Fat Cats Bring In Ants."
These phrases are general and are available on other free online sources. You may refer to these or create your own.
This article concludes here with all the relevant information taken from NCERT and other authorised sources on the periodic table of chemistry. For more related information, check out the official website of Jagran Josh.
Related: